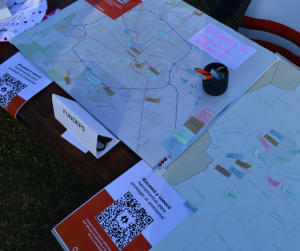
Last Sunday, April 24, 2022, within the framework of Earth Day, the “Córdoba Repara” Festival was held on the Enchanted Island of Sarmiento Park and Fundeps was part of it through a stand with an interactive and collaborative proposal. with the audience.
“Below, we offer a google translate version of the original article in Spanish. This translation may not be accurate but serves as a general presentation of the article. For more accurate information, please switch to the Spanish version of the website. In addition, feel free to directly contact in English the person mentioned at the bottom of this article with regards to this topic”.
The event organized by the Youth Directorate of the Municipality of Córdoba and the Free University of the Environment in conjunction with environmental organizations in the city, aimed to raise awareness about caring for the environment, reduction, reuse, recycling and recovery of waste and objects and the consumption of sustainable products made by local entrepreneurs. All this was manifested through different activities such as live shows, spaces for dialogue, organization stands, vegan, vegetarian and agroecological food stalls, reception of recyclables, collection of blankets and coats to donate and a space dedicated exclusively to the Club of Repairers x Córdoba.
Our proposal consisted of collectively building two maps, one of the city of Córdoba and another of the province, where the people who circulated indicated what environmental problems they knew (or suffered from). From the dialogue with each one of the people and from our maps, environmental problems emerged that are repeated throughout the city and the province, and that are also reiterated over time.
The community that participated, mostly residents of different neighborhoods and areas of the city, identified very similar problems, such as the lack of differentiated waste collection, the existence of open-air dumps throughout the city and especially in the area of bypass, the lack or malfunction of sewers and sanitation in general, the contamination of the Suquía River and neighborhood streams, the contamination produced by Porta Hermanos, the poor/lacking urban planning, the existence of neighborhoods in Córdoba without drinking water, among others. For their part, those who live on the outskirts of the city or other localities such as Mendiolaza, Villa Carlos Paz, Villa Allende, Río Ceballos, La Calera, Río Primero, Segundo, Tercero and Cuarto, Juarez Celman, Punilla, Coronel Moldes, Bell Ville , among others, stated that the main environmental problems are related to clearing, fumigation with agrochemicals, quarrying, contamination of water resources, open-air dumps, fires, floods, and conflicts arising from the Punilla and Paravachasca highways.
At the same time, the lack of citizen participation in environmental matters that manifests itself in all problems also emerged as a concern. They also noted the existing barriers whether in access to public information, access to justice or in the decision-making process.
We were able to observe and analyze that despite the extension and diversity that the city and the province of Córdoba have, the environmental problems are very similar and are repeated in each territory, in addition, that none of them is new, on the contrary, they are repeated and they are accentuated with the passing of the years. For these reasons, we believe that it is necessary to continue working to find alternatives to the form of “development” that has been carried out, while it is imperative and fundamental to strengthen the mechanisms of citizen participation and that the State assumes a true commitment in that sense.
More Information
- We ask the Senate to incorporate new principles into the General Environmental Law
- We request information from the Ministry of Environment of the Nation
- Advisory Opinion of the IACHR on the environment and human rights
Author
Ananda Lavayen
Contact
Juan Bautista Lopez, juanbautistalopez@fundeps.org