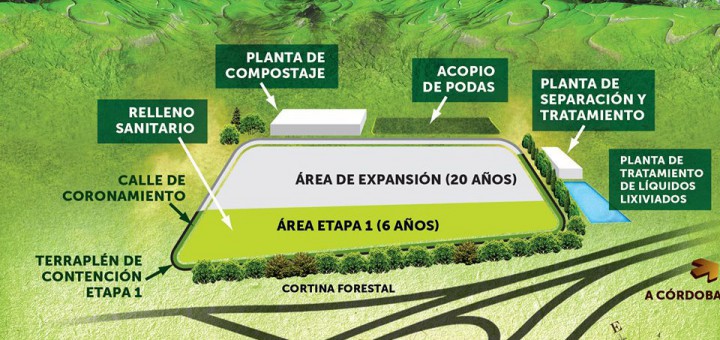
The project “Centro Ambiental Carlos Paz” presents serious irregularities and violates environmental regulations and participation. It would affect Lake San Roque and would not be a definitive regional solution to the historical problem related to the integral management of solid urban waste.
“Below, we offer a google translate version of the original article in Spanish. This translation may not be accurate but serves as a general presentation of the article. For more accurate information, please switch to the Spanish version of the website. In addition, feel free to directly contact in English the person mentioned at the bottom of this article with regards to this topic”
In the province of Cordoba, our officials continue to fail to provide an adequate and committed response to the problem of solid urban waste management. As in the elaboration of many other public policies deaf ears are made to the recommendations of science, technology and the needs of the citizens.
The management of urban solid waste is considered one of the main environmental problems of our society. And as a consequence of this, Argentina has an Integrated Management Program for Urban Solid Waste (GIRSU) -AR-L1151 financed by the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB).
The Program finances works for the integral management of urban solid waste (MSW) and the recovery of degraded areas due to the poor disposition of such residues. The total cost of the program is 150 million dollars within the same is the Environmental Center Villa Carlos Paz, whose name is already biased since it would be more accurate to talk about a landfill. A landfill is a place destined to the final disposition of trash, in which multiple measures are taken to reduce the impacts to the environment. In short, it seeks to reduce and isolate waste and develop mechanisms to treat liquids and gases produced by the decomposition of organic matter.
The questioned Environmental Center Villa Carlos Paz pretends to be a landfill where there is now an open dump. The autoconvocado neighborhood group, opposes the construction of the landfill in the selected place and approved by the Secretariat of Environment and Climate Change of Cordoba. Since the beginning of this year we are working together with neighbors and neighbors of the area. The reasons why we require the relocation of this project of more than 200 million pesos are varied. The guidelines of science and technology have not been followed for the elaboration and construction of this type of works and are violating environmental norms and citizen participation.
First, the environmental impact study (EIA) presents inconsistencies.
* Probable outdated baseline studies: There is a high probability of a mismatch of baseline description of water quality, soil, air as a function of the behavior of natural and environmental variables and impacts evaluated . The exact date of its elaboration is not known, but the EIA was presented by TecnoMak S.A. On March 30, 2015, had an opinion of the Technical Interdisciplinary Committee on February 29, 2016 and was submitted to a public hearing on April 6 of that year. In this context, both for the instance of citizen participation and for the execution of the work, the study was done in a context that is not the current one.
* Lack of clarity on the basis for the selection of the location of the work: it is objectionable the justification of the choice of the farm to carry out the works. To carry out the project TecnoMak S.A. Considered three possible properties, however it is unknown the fundamentals by which it was chosen for its location in the building of the current open dump. Neither are the reasons why the other two alternatives were ruled out.
* Possible impacts to the lake and a reserve: The situation is aggravated by the fact that it is intended to build a few meters from Lake San Roque on land that may have a greater propensity to seep or leach into the water and adjoining a protected natural area Natural Reserve La Calera).
* Use of outdated census data: The EIA uses data from the 2008 national population census, with one being carried out in 2010, which shows considerable changes in the number of inhabitants of the area.
Secondly, the resolutions of the administration that establish the useful life of the project are not clear. The first opinion of the Interdisciplinary Technical Commission of the Environment Secretariat (February 29, 2016) suggests that “the draft module for the final disposal of MSW will be maximum for a use of six years.” It also recommends that the use of the module for the final disposal of RSU receives only the waste from the town of Villa Carlos Paz. Following the public hearing held on April 6, 2016, and without public prefeasibility studies, a second opinion of the ITC decided to extend the useful life of the project to twenty years, as well as the number of communes reached To the towns of Villa Río Icho Cruz, Mayu Sumaj, Cuesta Blanca, Tala Huasi, Cabalango and Malagueño. In summary, the reasons for which this decision was taken are not known, the plane with the exact coordinates where the Landfill and the total number of projected modules.
Thirdly, the right to participation of citizens living within the area of influence of the project was affected. The art. 67 of Law 10,208 establishes that the public hearing process must be carried out in the area of influence of the project and open participation. In this case, the public hearing was convened only in Villa Carlos Paz (Department of Punilla), and one of the areas most affected by the proximity of the property is the municipality of Malagueño, belonging to the Department of Santa Maria. In addition, the possibility of convening a popular consultation was not foreseen, considering the possible categorization of the project as having a high environmental complexity (article 68, law 10,208).
This alarming project has an environmental license approved by the Ministry of Environment of the Province, and the EIA has not been prepared in strict compliance with the current regulatory framework. Socio-environmental conflict is imminent and works can begin at any time.
The excessive growth in the volume of waste in today’s society is endangering the capacity of nature to maintain our needs and those of future generations. Population and consumption grow, and as a consequence, also the amount of garbage we generate. The problem is that the space does not grow and that we are not giving the right treatment.
We have submitted requests for information to the Secretary of Environment of the Province of Córdoba, the Municipality of Malagueño and the Municipality of Villa Carlos Paz. In addition, on May 8, we approached a note to IDB officials in Argentina responsible for following up on the program by letting us know about these concerns.
We demand transparency, accountability and coherence in government acts. We need integral and long-term solutions for the integral management of solid urban waste. Our officials are obliged to comply with current standards and to ensure that human rights and the environment are respected. It is not possible to make decisions democratically at any cost and regardless of the conditions.
More information
- Advances and challenges in the Villa Carlos Paz Environmental Center Project
- Conflicts around the construction of the Villa Carlos Paz Environmental Center
- The problem of solid urban waste in Córdoba
Contact
Male Martinez, malemartinez@fundeps.org
María Victoria Gerbaldo, victoriagerbaldo@fundeps.org