“Below, we offer a google translate version of the original article in Spanish. This translation may not be accurate but serves as a general presentation of the article. For more accurate information, please switch to the Spanish version of the website. In addition, feel free to directly contact in English the person mentioned at the bottom of this article with regards to this topic”
The year 2017 began with important and promising news for the Gasification Project of Localities of the Interior of the Province of Córdoba, better known by the people of Córdoba as the “main gas pipeline project”. During the first days of January, the Governor of Córdoba Juan Schiaretti and President Mauricio Macri were present at the inauguration of a Pressure Reducing Plant in La Calera, work carried out by the Brazilian company Odebrecht within the framework of the systems awarded to it after the public tender launched in 2015. The reduction plant constituted the first section inaugurated by the Córdoba-Gran Córdoba Ring System, comprised of 52 kilometers of gas pipelines. reinforcement, and that will benefit 300 thousand inhabitants of both Córdoba and La Calera and of Saldán, Villa Allende, Mendiolaza, Malagueño and Malvinas Argentinas, according to official information.
The presence of Macri at the inauguration of the work represented a gesture of political support for the Schiaretti government. Especially taking into account the strong questions and criticisms received by the provincial government for the involvement in this project of the Brazilian construction company Odebrecht, involved in a corruption scandal in Brazil and other Latin American countries, even in Argentina. Despite these questions, the Schiaretti government always defended the participation of the company by resorting to the debatable argument that the corruption events in which it is involved occurred between 2004 and 2013, while the tender in Córdoba was carried out only in 2015.

However, after a few days the project suffers a major setback: Schiaretti announces that, due to delays in obtaining loans from Chinese banks, 4 stretches of gas pipelines would be re-tendered to avoid postponing the start of the works in said sections, but in this case with the Province’s own financing. Recall that of the 10 trunk systems that were defined in 2015, 4 were awarded to Transitory Business Unions (UTEs) made up of Argentine and Chinese companies and financed by Chinese banks (ICBC and Bank of China); and the remaining 6 were awarded to Odebrecht (at first it was said that the Brazilian company would present its own financing for the start of the work, but finally this was not the case, making the province have to resort to indebtedness to start the works).
Thus, criticisms of the link with Odebrecht in the work will be added to questions about the delays in Chinese financing; the lack of relevant explanations regarding the reasons for the fall in financing; the need to re-tender the work and the decision of the provincial government to go back to the market to borrow to finance the work and even for the substantial increase in the cost of the work, which went from a budget of 8,600 million pesos in 2015 to 12,480 million pesos at the beginning of 2017 (an increase of 45% in almost two years).
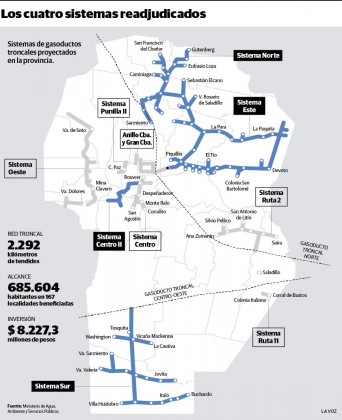
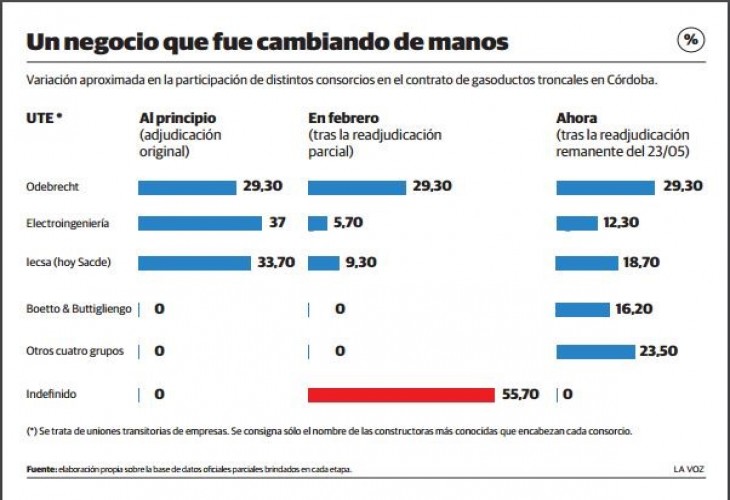
After a new call for bids in February, in March the works of the four aforementioned systems were re-awarded to the same UTEs that had won in the first tender. In turn, the government issued a new batch of public securities for 460 million dollars to finance the start of works in the 4 tranches of the project, with the financial agent of Banco de Córdoba (Bancor).
Although in that same month of March advances were announced in the negotiations with the Chinese banks to finish making the committed credits for the work, surprisingly on April 21 the Governor Schiaretti announced the definitive fall of the Chinese financing and the signing of a decree that rendered ineffective the adjudication of the works of the 4 corresponding trunk systems. While Schiaretti himself blamed the Chinese banks for the fall in funding, arguing that they raised conditions “leonine, unacceptable to Cordoba and the national government,” the fact is that the government never made clear the true reasons and reasons that led to the fall of Chinese financing.
In this way, the government of Córdoba decided to launch a new tender for 437 million dollars for the construction of the 4 gas pipeline systems, which now in the new call would become 8 systems (in addition to the 6 remaining systems already awarded to Odebrecht ) and whose financing would come from the same province. In this case, the allocation of the new systems fell to national companies.
In early May, and despite criticism from the opposition, the provincial legislature approves a bill that enables new changes in the pipeline project: the negotiations with Chinese banks to finance 4 of the trunk systems are terminated, and it is approved that it is now the provincial government itself that must obtain the totality of the funds to complete the work (ratifying in this way the authorization granted by law 10,339 that enabled operations to take public credit to carry out the works). Just a few days later, the government made official through a decree published in the Official Gazette, a new debt collection for 450 million dollars to finance the work. By the end of June, Schiaretti himself would announce through his Twitter account that the province had obtained the total financing for the work through the placement of bonds in the international capital market.
In short, this strategic project for Córdoba that was going to have in the beginning with financing provided or managed by international actors (initially through the National Bank of Economic and Social Development of Brazil -BNDES-, then through Chinese banks and own financing provided by the Odebrecht company) to depend exclusively, for its concretion, on the province’s own resources or obtained through debt through the issuance of government securities.
The second half of the year would be marked mainly by the progress of the work (according to the government by the end of the year 14% of the work had been completed and the work was planned to be completed by mid-2019), but also by the constants and recurring questions from sectors of the opposition and civil society in relation to the project. Especially after Córdoba was mentioned in the framework of the Lava Jato case as one of the destinations where the Odebrecht constructure paid bribes in Argentina.
Although the national government of Mauricio Macri began a campaign to review and investigate the possible involvement of Odebrecht in the payment of bribes in numerous public works projects in Argentina (which even led the national government to suspend the company to carry out works at a national level), the gas pipeline project in Córdoba was strangely excluded from said revision and the relevant explanations were never provided to justify such exclusion. Even the company continues to operate in the province despite its suspension at the national level (its main work is precisely that of gas pipelines in Córdoba) and the requirements from the opposition that the same be done at the provincial level. Given the lack of answers at the national level, some opposition legislators traveled to Brazil in October of this year to ask the prosecutors of the Lava Jato case to investigate the link between the Brazilian company in the payment of bribes in the framework of the bidding process in 2008 for the construction of trunk pipelines.

In this way, between marches and counter-marches, the balance of 2017 in relation to the trunk gas pipeline project throws little light and many shadows and suspicions in relation to the transparency and execution of the project. Not only because of the never entirely clear fall of Chinese financing at the beginning of the year but also, and above all, because of the way the provincial government has handled the involvement of the construction company Odebrecht in the work and the numerous causes of corruption that splash throughout Latin America and even in Argentina itself. Although the government of Schiaretti has detached the company from any kind of connection with the possible delivery of bribes and corruption in the bidding of the work (even with the support of the national government of Macri itself that has initiated a kind of “Crusade” against the Brazilian company for its actions in the country during the Kirchner government), the truth is that the year that ends leaves many questions and aspects not clarified about the project.
Undoubtedly, 2017 has left a huge debt outstanding in terms of transparency and accountability in relation to this strategic and emblematic project for Córdoba. From FUNDEPS, we expect this debt to be paid in 2018.
More information
– Working Document: Transparency in the gasification project of localities in the interior of the province of Córdoba by Melanie Mackenzie – December 2017. FUNDEPS.
– Notes and publications of FUNDEPS in relation to trunk gas pipelines.
– Main gas pipelines in Córdoba: a work that advances in the shadow of corruption by Agustina Palencia – December 2017. El Entramado. FUNDEPS.
Image source
La Voz del Interior
Authors
Macarena Lourdes Mustafa / Voluntaria del Área de Gobernabilidad Global
Gonzalo Roza / Coordinador del Área de Gobernabilidad Global
Contact
Gonzalo Roza / Coordinador del Área de Gobernabilidad Global
gon.roza@fundeps.org








