The United Nations Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights concluded on September 28 the fourth report of Argentina on the implementation of the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights.
After an interactive dialogue with the Argentine delegation, the Analysis Committee was integrated The report was presented by the State and also the information by civil society organizations through the shadow reports.
“Below, we offer a google translate version of the original article in Spanish. This translation may not be accurate but serves as a general presentation of the article. For more accurate information, please switch to the Spanish version of the website. In addition, feel free to directly contact in English the person mentioned at the bottom of this article with regards to this topic”
Main conclusions
One of the central issues addressed by the Committee was the financial crisis, because in a context where poverty rates continue, policies to reduce social programs have been implemented, deepening the vulnerability of some social groups. The Argentine State was also questioned about the situation faced by its government institutions, the degradation of some ministries to secretariats, and about the appointment of the Ombudsman.
On the other hand, he expressed his concern for the repression of social protest and access to the land of native peoples. In addition, although the Committee congratulated the adoption of the Gender Identity and Equal Marriage Law in the country, it drew attention to the lack of access to work and harassment in the educational system for LGBTI people, people with disabilities, migrants and women. He also asked the State about youth unemployment, informal work, and several issues related to education (school dropout, sexual and reproductive education and teaching of native languages).
Find more information on public education and comprehensive sex education.
Equality between men and women
Argentine women are affected by the unpaid work of family care, the low rate of labor participation, lack of universal provision of social services and low representation in senior positions in various sectors (particularly justice and the private sector). Therefore, the Committee recommends strengthening legislative provisions and public policies with assigned budgets, aimed at achieving equal rights for men and women, including a public system of comprehensive care, the implementation of measures against social stereotypes that affect women and the promotion of reconciliation policies between work and family life.
On equal opportunities for women and LGBTI people in media organizations, you may be interested in the following link.
Sexual and reproductive rights
 Regretting that the bill of voluntary interruption of pregnancy was not approved, the Committee highlighted the high numbers of dangerous abortions in Argentina
Regretting that the bill of voluntary interruption of pregnancy was not approved, the Committee highlighted the high numbers of dangerous abortions in Argentina
and the obstacles to access to abortion in the causes foreseen by the current law, such as the lack of adequate medicines and the negative impact of conscientious objection by health professionals. He also highlighted the lack of a normative and institutional framework to guarantee adequate health services for intersex people.
Among its recommendations in this area, are the provision of contraceptive methods throughout the territory, as well as the adoption of effective measures for the effective implementation of the causes of non-punishable abortion in all provinces – under the provisions of the FAL ruling – and access to medications that allow a safe pregnancy termination. It also recommended the regulation of conscientious objection in order not to obstruct the rapid and effective access to abortion, with dignified treatment by health professionals for patients seeking access to abortion services, as well as not criminalizing women who resort to abortion. practice. Finally, it recommended adopting a normative and institutional framework to guarantee adequate health services for intersex people.
Violence against women
The Committee is concerned about the seriousness of violence against women and girls, with 251 femicides in 2017, despite some progress (such as the inclusion of the figure of femicide in the Criminal Code and the law of Integral Protection). For this, he urged the State to consider the needs of victims of gender violence in the judiciary, to implement free and specialized sponsorship services for women and to improve measures to guarantee the investigation, punishment and reparation of acts of violence , in order to achieve full protection for women and their children.
Feeding
 On this point, the Committee regretted the absence of an explicit constitutional recognition and protection of the right to food, the lack of implementation of the Family Agriculture Law No. 27,118, budget and personnel cuts in the family agriculture sector and the increase of people who depend on school and community dining rooms.
On this point, the Committee regretted the absence of an explicit constitutional recognition and protection of the right to food, the lack of implementation of the Family Agriculture Law No. 27,118, budget and personnel cuts in the family agriculture sector and the increase of people who depend on school and community dining rooms.
He also expressed concern about the increase in the rates of overweight and obesity, the absence of state measures to reduce the consumption of sugary drinks and the lack of adequate regulation to restrict the advertising of unhealthy foods.
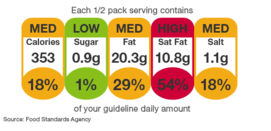
In this sense, its main recommendations were to adopt a normative framework that expressly recognizes the right to food and that guides public policies that ensure a healthy, nutritious and sufficient diet, especially for disadvantaged groups. This includes ensuring the effective implementation of the Family Farming Law and taking effective measures to discourage the consumption of foods and beverages harmful to health. At this point, it was even recommended to increase the tax on sugary drinks, strengthening the regulation of the Argentine Food Code in terms of front labeling of foods, including information on sugar in the products, and implement restrictions on the advertising of food and drinks harmful to health, particularly those intended for children and adolescents.
Learn more about food labeling and consumption of sugary drinks.
Health and tobacco use
The high consumption of tobacco has a great negative impact on the health of people in Argentina. The regulation of taxes on tobacco is insufficient and the regulation on advertising campaigns is precarious, so the Committee recommended to our State to adopt more robust measures for the prevention of consumption. Among these, mention is made of the tax increase at a level sufficient to have a deterrent effect on tobacco consumption, the prohibition on advertising, and information campaigns on the negative impact of tobacco on health, with emphasis on the protection of tobacco products. children and youth
In addition, he urged the State to ratify the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control and to adjust the internal regulations on the advertising of tobacco products to the standards established in this Agreement.
Here you can read more about the tobacco control framework agreement.
Mining and the environment
 The use of certain unconventional methods of exploitation of hydrocarbons, such as fracking, and the local impact of these forms of exploitation were another concern of the Committee. In particular because of the negative impact they can have on the environment, water and health. Therefore, the country was recommended to adopt a fracking regulatory framework that includes assessments of its impact in all provinces, prior consultations with affected communities, and appropriate documentation of its effects on air and water pollution, emissions radioactive, the risks to health and safety at work, the effects on public health, noise pollution, light and stress, seismic activity that can trigger, threats to agriculture and soil quality, and to the climate system.
The use of certain unconventional methods of exploitation of hydrocarbons, such as fracking, and the local impact of these forms of exploitation were another concern of the Committee. In particular because of the negative impact they can have on the environment, water and health. Therefore, the country was recommended to adopt a fracking regulatory framework that includes assessments of its impact in all provinces, prior consultations with affected communities, and appropriate documentation of its effects on air and water pollution, emissions radioactive, the risks to health and safety at work, the effects on public health, noise pollution, light and stress, seismic activity that can trigger, threats to agriculture and soil quality, and to the climate system.
Agriculture, healthy environment and health
The increase in the use of pesticides and herbicides that include glyphosate is worrisome, despite the serious adverse impacts on health and the environment of many of them, indicated as probably carcinogenic by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). ) of the World Health Organization.
In this regard, the Committee recommended that Argentina adopt a regulatory framework that includes the application of the precautionary principle regarding the use of harmful pesticides and herbicides, particularly those that include glyphosate, to prevent negative health impacts from its use and in the degradation of the environment.
On the application of agrochemicals, you may be interested in the following link.
Writer: Mayca Balaguer