Public consultations begin on the new IDB environmental and social policy
The Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) began the process of public consultations on the new Framework for Environmental and Social Policy. It will have both face-to-face and virtual instances and will be extended throughout the year 2020.
“Below, we offer a google translate version of the original article in Spanish. This translation may not be accurate but serves as a general presentation of the article. For more accurate information, please switch to the Spanish version of the website. In addition, feel free to directly contact in English the person mentioned at the bottom of this article with regards to this topic”.
With a statement on its website, the IDB announced the start of virtual and face-to-face public consultations on the draft of the new framework for environmental and social policy. According to the bank, this new framework aims to strengthen the environmental and social sustainability of the bank’s operations and, in turn, be more effective in responding to the challenges faced by the countries of the region to achieve the long-awaited growth. sustainable.
The Environmental and Social Policy Framework contemplates safeguards policies, lessons learned and good practices accumulated over the years. In addition, the policy mentions the bank’s commitment to environmental and social sustainability, and the 10 performance standards that borrowing member countries must meet.
Also, the draft policy contemplates environmental and social risks and impacts and highlights advances in human rights, gender equality, non-discrimination and stakeholder participation.
According to the consultation plan approved by the IDB Executive Board, the public consultation process will be significant, inclusive and transparent. However, a large part of civil society that has been working on agendas linked to the IDB over the last few years doubt that this is really the case, being guided by the bad experiences of the most recent public consultations carried out by the institution, which They characterized by their shortcomings in terms of public participation and transparency.
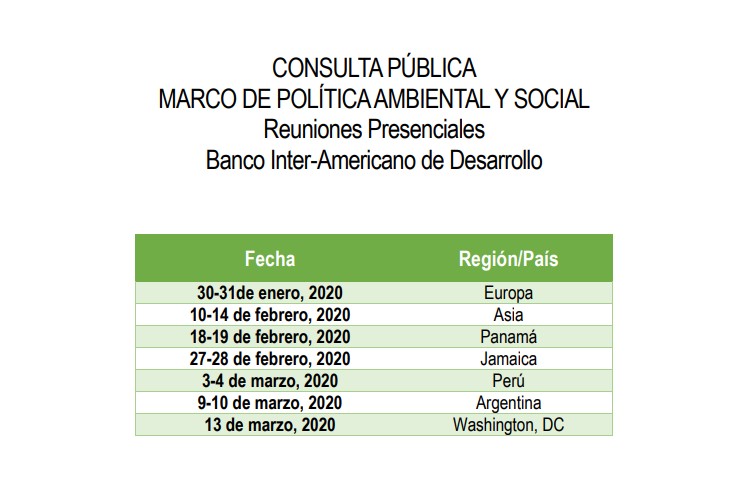
In-person consultation processes will take place at the Bank Headquarters in Washington D.C. and in some countries of Latin America and the Caribbean, Europe and Asia. Those interested in participating in face-to-face consultations may do so by registering here.
On the other hand, those who want to participate in virtual consultations, can send comments on the draft of the new policy through the website www.iadb.org/es/mpas or by sending an email to bid-mpas@iadb.org. The first phase of comments can be made until April 17.
Why is it important to participate?
For several reasons, it is necessary that civil society, citizens and, above all, indigenous communities and communities affected or potentially affected by IDB or IDB Invest operations actively participate in this process, contributing their experience and its recommendations and suggestions regarding the environmental and social safeguards of the institutions.
First, because both the IDB and the IDB Invest are, today and despite the diversification of financial actors operating in the region, key actors in financing for development in Latin America and the Caribbean. According to the Bank itself: in 2018, with a historical amount of US $ 17,000 million approvals, the IDB and the IDB Invest were consolidated as the main source of multilateral financing for Latin America and the Caribbean. The IDB approved a total of 96 sovereign guaranteed loan projects for a total financing of more than US $ 13.4 billion, and disbursed more than US $ 9.9 billion. In turn, 2018 was a record year for IDB Invest, with approvals of US $ 4,000 million, 26% more in volume and 21% more in number of transactions than the previous year. The IDB Invest extended its support to sectors such as infrastructure and Fintech, adding to education, tourism, water and sanitation, transport and energy. In the case of Argentina, the IDB has historically been the main multilateral partner for the country’s development, with an average of recent annual approvals of US $ 1,360 million. The current active portfolio with the public sector is 54 operations for an approved amount of US $ 9,206.4 million and an unpaid balance of US $ 3,874.7 million, according to the information provided by the Bank itself.
Second, because a robust and effective system of environmental and social safeguards is key to avoiding the impacts at the socio-environmental level that, in many cases, bring infrastructure projects financed by institutions such as the IDB or the IDB Invest. When the design, application or implementation of environmental and social safeguards fails in these types of projects, the impacts and consequences especially in the communities involved are often complex, and unfortunately in many cases, irreversible. Cases such as Camisea in Peru or Hidroituango in Colombia reflect the bitter consequences of the bad, or even the lack of application of socio-environmental safeguards in projects financed by the IDB Group.
Third, because an active, informed, responsible and coordinated participation by the key actors of civil society and the indigenous and affected communities of the region would contribute to the objective of avoiding a possible (and latent) dilution of the system of environmental and social safeguards from both the IDB and the IDB Invest. Recent experiences of dilution of environmental and social regulatory frameworks after review and “modernization” processes not only in related institutions such as the World Bank or the International Finance Corporation (IFC), but also in the national regulatory systems of the countries of The region clearly reflects a trend that the IDB Group seems not to want to escape.
Sofia Brocanelli
Gonzalo Roza
Gonzalo Roza, gon.roza@fundeps.org